CS 115 Lab 5, Part D: Find turning points
[Back to lab instructions]
Introduction
You now have a solution that can detect if the second point of two consecutive points of a
sequence is moving downward or upward. In this version, you will detect the turning
points. That is, you will determine if we have just seen a peak or a valley.
We defined these terms in the pre-lab.
You will color points that are valleys in blue and points that are peaks in red.
These points will have radii of 3, instead of a radius of 1 like the other points.
Instructions
- Create a new Python file named lab05d.py:
"""
Program: CS 115 Lab 5d
Author: Your name
Description: This program draws a graph and identifies turning points.
"""
from graphics import *
def main():
window_height = 600
window = GraphWin('Graph', 800, window_height)
# Open the input file and read the number of points
pointsfile = open("points-test.txt", "r")
num_points = int(pointsfile.readline())
x = 20
first_y = int(pointsfile.readline()) # get the first y-coordinate
first_point = Point(x, window_height - first_y)
x += 10
second_y = int(pointsfile.readline())
second_point = Point(x, window_height - second_y)
########## Complete this code: draw the line between these 2 points
########## Fix this if-statement
if second_y is greater than first_y
increasing = True
else:
increasing = False # in other words, we're decreasing
############
# Complete this code:
# Use the value of "increasing" to determine and print whether the first
# point is a peak or a valley.
# If it's a peak, draw it in red. If it's a valley, draw it in blue.
# Use a radius of 3 instead of 1.
############
# Update first_y and first_point
first_y = second_y
first_point = second_point
for i in range(2, num_points): # already did first 2
# Read the next point and update x
x += 10
second_y = int(pointsfile.readline())
second_point = Point(x, window_height - second_y)
############
# Copy this code from Part C
# draw the line between first_point and second_point
# draw a circle centered at first_point with radius 1
############
############
# Complete this code:
# if the sequence has been increasing:
# if first_y is larger than second_y:
# we must be at a peak and about to go downward
# draw a red circle centered at first_point with radius 3
# print that this point is a peak
# if the sequence has been decreasing:
# if first_y is smaller than second_y:
# we must be at a valley and about to go upward
# draw a blue circle centered at first_point with radius 3
# print that this point is a valley
############
############
# Think about why this works!
increasing = second_y > first_y
############
# second_point becomes the first point of the next line
first_y = second_y
first_point = second_point
###### Complete this code
# Decide and print whether first_point is a peak or a valley
# Draw the appropriate circle
window.getMouse()
window.close()
main()
- Complete the code where indicated. Your graph should look like the following:
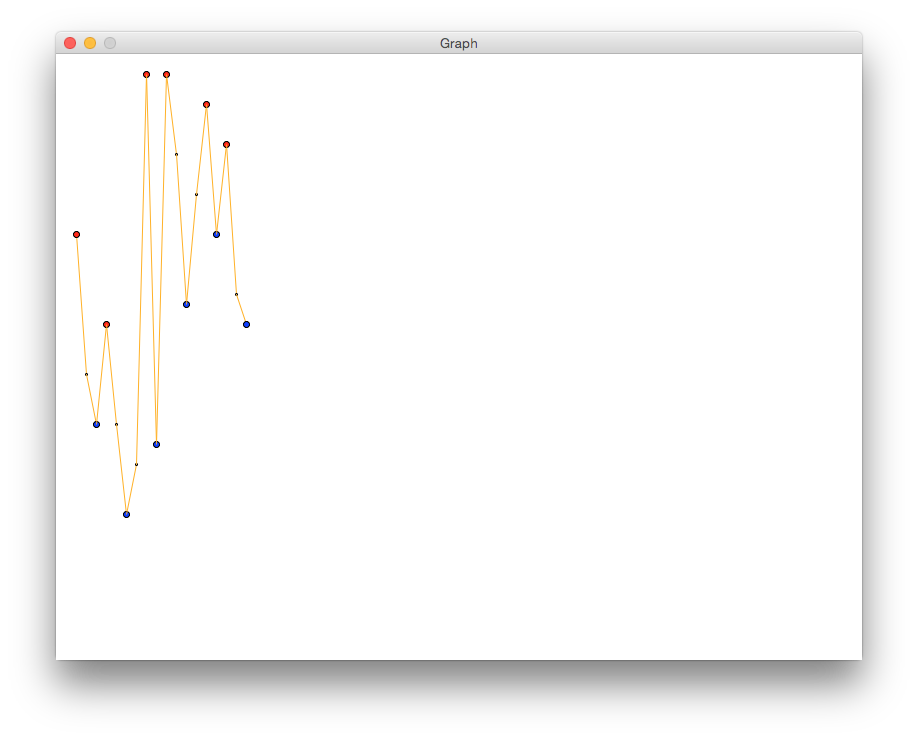
- Add print statements to generate this output:
420 is a peak.
230 is a valley.
330 is a peak.
140 is a valley.
580 is a peak.
210 is a valley.
580 is a peak.
350 is a valley.
550 is a peak.
420 is a valley.
510 is a peak.
330 is a valley.
- In your code, modify the line that opens the input file to:
pointsfile = open("points.txt", "r")
Rerun your program. It should identify 6 peaks and 7 valleys. When that is working, call an instructor to demo your code.
- Make sure that your name is at the top of the file and the docstring has been updated.
- Continue to Part E.
